What is a Pt100 Sensor?
A Pt100 sensor is a type of platinum resistance temperature detector (RTD) that has a resistance of exactly 100 ohms at 0°C. The term “Pt” stands for platinum, and “100” refers to the resistance value in ohms. Pt100 sensors are widely used in industrial temperature measurement thanks to their excellent accuracy, repeatability, and long-term stability.
Pt100 probes are used for measuring temperature in process control, HVAC, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage production, automotive testing, and energy generation applications. This guide explains everything you need to know: how they work, temperature ranges, standards, wiring setups, colour codes, calibration, connectors, and how they compare with thermocouples.
We offer a wide range of Pt100 sensors designed and manufactured in the UK to meet industry standards. For applications requiring higher resistance, we also supply Pt1000 sensors.
Our Most Popular Pt100 Sensor Styles
Mineral InsulatedPt100 Sensors
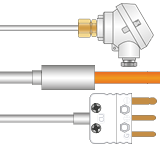 Our most popular style. Ideal for most temperature measurement tasks. Wide range of cable and termination options including pot seals, plugs, and terminal heads.
Rigid Stem
Our most popular style. Ideal for most temperature measurement tasks. Wide range of cable and termination options including pot seals, plugs, and terminal heads.
Rigid StemPt100 Sensors
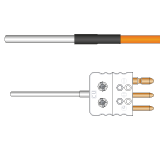 Best suited for applications requiring short probes under 50 mm. Rated up to 250°C with a full range of termination types.
Handheld
Best suited for applications requiring short probes under 50 mm. Rated up to 250°C with a full range of termination types.
HandheldPt100 Sensors
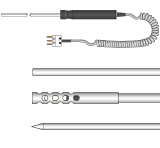 Designed for field and lab use. General-purpose handheld sensors for immersion, surface, or air temperature readings.
Surface Measurement
Designed for field and lab use. General-purpose handheld sensors for immersion, surface, or air temperature readings.
Surface MeasurementPt100 Sensors
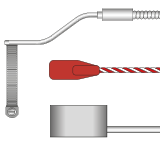 Ideal for pipework, vessels, and flat surfaces. Includes self-adhesive patch sensors, magnetic sensors, and clamp-on types.
Ideal for pipework, vessels, and flat surfaces. Includes self-adhesive patch sensors, magnetic sensors, and clamp-on types.
How Does a Pt100 Sensor Work?
Pt100 sensors rely on a simple but precise principle:
- Platinum changes resistance with temperature.
- As temperature rises, the resistance of the platinum element increases almost linearly.
- Instrumentation such as panel meters or controllers convert this resistance into an accurate temperature reading.
Quick Facts:
- Resistance at 0 °C = 100 Ω.
- Temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) ≈ 0.385 Ω/°C (IEC 60751).
- Output signal: resistance, measured directly or via transmitters.
Explore our in-depth Thermocouple & Resistance Thermometry Guide — a technical resource developed for engineers and specifiers. Covers sensor selection, installation practices, standards and tolerances, colour codes, wiring configurations, sensor theory and more.
Temperature Ranges for Pt100 Sensors
The usable range depends on the construction of the probe. Two of the most common industrial versions are rigid stem Pt100 sensors and mineral insulated (MI) Pt100 sensors.
| Probe type | Typical Temperature Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid Stem Pt100 | -75 °C to +250 °C | Robust stainless steel sheath; ideal for general industrial use and immersion in processes. |
| Mineral Insulated Pt100 (MI) | -100 °C to +600 °C | Sheath allows bending and custom routing; better vibration resistance and higher temperature capability. |
Key Considerations:
- Rigid stem: chosen where durability and mechanical strength matter more than flexibility.
- MI versions: preferred in demanding environments (e.g., high temperatures, vibration, or when routing through tight spaces).
- Both probe types can be supplied with different diameters, lengths, and connection heads or cables depending on the application.
Standards and Accuracy
Pt100 sensors are manufactured to international standards to ensure reliable, repeatable measurements.
- IEC 60751 is the primary global standard.
- Accuracy limits apply to the sensor element itself — assembled probes may introduce additional error depending on construction and application.
| Class | Accuracy at 0ºC | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | ±0.15 °C | General industrial measurement, process control |
| Class B | ±0.30 °C | Standard applications where cost is important |
| 1/3 | ±0.10 °C | Higher-accuracy process monitoring, QA checks |
| 1/5 | ±0.06 °C | Precision manufacturing, pharmaceutical & biotech |
| 1/10 | ±0.03 °C | Calibration labs and critical reference standards |
Pt100 Wiring Configurations
Different wiring schemes are used to minimise errors caused by lead resistance.
- 2-wire: simplest, but lead resistance adds error.
- 3-wire: most common in industrial applications; compensates for most of the error caused by lead resistance (assuming wires are equal), giving a good balance between accuracy and cost.
- 4-wire: best accuracy; eliminates lead resistance completely, often used in labs and calibration.
Pt100 Colour Codes
Correct wiring depends on industry standards:
| 2-wire | 3-wire | 4-wire |
|---|---|---|
| Red / White | 2×Red, 1×White | 2×Red, 2×White |
Pt100 vs Thermocouples
Both Pt100 sensors and thermocouples are widely used — but they serve different purposes.
Advantages of Pt100's
- High accuracy (down to ±0.1 °C).
- Excellent long-term stability.
- Defined international standards.
Advantages of Thermocouples
- Much wider temperature range (up to 1800 °C).
- Faster response for certain types.
- Lower cost at very high temperatures.
| Feature | Pt100 | Thermocouple |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | ±0.1–0.3 °C | ±1–2 °C typical |
| Stability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Range | -100 to +600 °C | -200 to +1800 °C |
| Signal | Resistance (Ω) | Voltage (mV) |
| Cost | Moderate | Low–High (type dependent) |
Calibration of Pt100 Sensors
Calibration ensures measurement accuracy over time.
Methods:
- Ice bath reference at 0 °C.
- Dry block calibrator.
- Comparison against a certified reference thermometer.
Best practices:
- Calibrate across multiple temperature points (e.g., 0 °C, 100 °C, 200 °C).
- Follow ISO calibration requirements if used in regulated industries.
Extension Cables and Connectors
Correct cable and connector selection ensures reliable performance.
Cables:
- PVC insulated (up to +105 °C).
- PTFE insulated (up to +250 °C).
- Fibreglass insulated (up to +400 °C).
Connectors:
- Miniature and standard RTD connectors.
- Industrial terminal heads.
Applications of Pt100 Sensors
Pt100 sensors are trusted wherever accuracy and stability are essential:
- Chemical and petrochemical processing.
- HVAC and building controls.
- Food and beverage production.
- Pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturing.
- Power plants and energy systems.
- Automotive test benches.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a Pt100 resistance thermometer, and how does it work?
A resistance thermometer measures temperature by detecting changes in electrical resistance. The "Pt" stands for platinum, the material used in the sensing element, and "100" refers to the resistance value of 100 ohms at 0°C. As the temperature changes, the resistance of the platinum element varies, allowing for accurate temperature measurements. - How accurate are Pt100 sensors?
Pt100 sensors offer high accuracy and stability, with industrial-grade elements ranging from Class B (±0.3ºC at 0ºC) to Class A (±0.15ºC at 0ºC). Higher precision options, such as 1/10 class elements, provide an accuracy of ±0.03ºC at 0ºC. These sensors are widely used in industrial, laboratory, and scientific applications requiring high precision. Additionally, we offer calibration services in our UKAS accredited laboratory. - What is the temperature range for Pt100 sensors?
The temperature range of an RTD sensor depends on factors such as the construction, sheath material and insulation used in the construction. While some platinum elements can withstand temperatures up to 850°C, the overall sensor design will limit the maximum temperature rating. Please check the product specifications for the exact temperature range based on the sensor’s construction. If you need any advice, our engineers are happy to assist! - What is a Pt100 used for?
Resistance thermometers are widely used for accurate temperature measurement in industrial, scientific, and commercial environments. Common applications include process control, laboratory testing, HVAC systems, and food and beverage production. Their precision and stability make them ideal for situations where consistent and repeatable readings are critical. - Is a Pt100 the same as an RTD?
Yes, a resistance thermometer is another term for an RTD, or Resistance Temperature Detector. The terms are often used interchangeably, although \"resistance thermometer\" is more common in formal or technical literature. RTDs typically use platinum elements (such as Pt100) to measure temperature through changes in electrical resistance. - What types of resistance thermometers do you offer?
We offer a wide range of resistance thermometers, including Pt100 and Pt1000 sensors in 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configurations. Options include surface sensors, immersion probes, ATEX-approved sensors for hazardous areas, and custom assemblies tailored to OEM or industrial applications. All are manufactured in the UK to ISO 9001 standards. - How do I choose between a Pt100 and a Pt1000 resistance thermometer?
Pt100 sensors have a resistance of 100 ohms at 0°C, while Pt1000 sensors have 1000 ohms at 0°C. Pt1000s are often preferred for longer cable runs because of their higher signal-to-noise ratio, whereas Pt100s are more widely used in industrial systems and instrumentation. The choice depends on the measurement environment and your system’s compatibility. - Do Pt100 sensors require calibration?
Yes, for critical applications or compliance with quality standards, regular calibration of resistance thermometers is recommended. We offer calibration services through our UKAS-accredited laboratory to ensure traceability and measurement confidence. Certificates are available with each calibrated sensor upon request.

 France
France Germany
Germany Spain
Spain Netherlands
Netherlands Italy
Italy Hungary
Hungary United States
United States Australia
Australia