What is a Type K Thermocouple? – Chromel Alumel Temperature Sensor
Type K (NiCr–NiAl) | IEC 60584-1 Standard

Type K thermocouples (Chromel–Alumel) are the most widely used and cost-effective industrial temperature sensors. They offer a wide operating range, fast response, and excellent resilience, making them the first choice for engineers specifying general-purpose thermocouple probes across multiple industries.
Type K can measure up to 1,100°C in continuous operation, with short-term limits extending to 1,200°C. However, at temperatures above 800°C, oxidation can degrade performance over time, causing drift or decalibration. They are not suitable for reducing or sulphurous atmospheres without appropriate sheath protection. While often used in nuclear applications due to radiation resistance, Type N thermocouples are recommended for better long-term stability under radiation exposure.
We manufacture Type K thermocouples in the UK
Available in mineral insulated, heavy duty, surface, miniature, ATEX/IECEx and custom configurations.
- Fast manufacture
- Custom lengths, diameters, sheath materials, end seals, cables etc.
- UKAS calibration available
Type K Thermocouple Sensors (UK Manufactured)
Choose from the categories shown below and custom build as required:
Type K Mineral Insulated Thermocouples
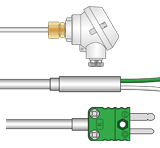
Rugged sensors, ideal for most applications. Vast choice of terminations e.g. pot seals, cables, connectors, heads etc.
Type K Swaged Tip Thermocouples
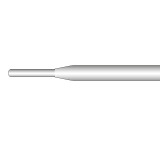
Fast response thermocouples ideal for industrial and other applications.
Type K Miniature Thermocouples
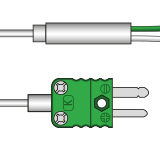
Ideal for precision temperature measurements where minimal displacement and a fast response is required.
Type K Heavy Duty Thermocouples
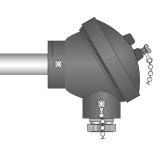
For industrial applications such as furnaces, kilns, ovens, boliers, flues etc. Many types of sheath material available.
General Purpose Type K Thermocouples
A wide range of thermocouples to suit many applications. Hand held, surface, bayonet, bolt, patch styles etc.
ATEX/IECEx Approved Type K Thermocouples
A large range of thermocouples with a variety of terminations such as pot seal, terminal heads etc.
Type K - Technical Data
What are the conductors of a Type K Thermocouple?
The positive conductor of a Type K thermocouple is NICKEL - CHROMIUM which is also known as: Chromel™, Thermokanthal KP*, NiCr, T1* and Tophel™, whilst the negative conductor is NICKEL - ALUMINIUM (magnetic which helps with identification) and is also known as: Ni-Al, Alumel™, Thermokanthal KN™, T2™, NiAl™.
How accurate is a Type K Thermocouple?
There are a few factors to consider when quoting the accuracy of a thermocouple, such as the tolerance class of any cables or connectors and the accuracy of the associated indicators or instrumentation. The following accuracy figures are for the thermocouple material that we use in the manufacture of our thermocouple sensors and correspond to the output tolerances stated within IEC 60584-1:
We offer UKAS accredited thermocouple calibration and other services to prove the accuracy of complete thermocouple probes and systems.
What is the temperature range of a Type K Thermocouple?
The design of any specific thermocouple sensor has an influence on the temperaure range of the sensor. Things such as sheath diameter and sheath material can be a limiting factor as well as associated cables, connectors, sealants etc. The following ranges are for the thermocouple material used in the manufacture of our thermocouples: Continuous: 0ºC to +1100ºC and Short Term: -180ºC to +1350ºC.
What is the output from a Type K Thermocouple?
A Type K Thermocouple generates an EMF according to the differential in temperature between the measuring junction and the reference junction. A detailed explanation can be found in our guide to how a thermocouple works. The specific EMF change per ºC in accordance with IEC 60584-1 can be found on our Type K Thermocouple Output Table, however, some approximate generated EMF change in µV per ºC change (referenced to 0ºC) are as follows: at 100ºC = 42µV, at 500ºC = 43µV and at 1000ºC = 39µV.
Explore our in-depth Thermocouple & RTD Guide — a technical resource developed for engineers and specifiers. Covers sensor selection, installation practices, standards and tolerances, colour codes, wiring configurations, sensor theory and more.
What is the Colour Code for a Type K Thermocouple?
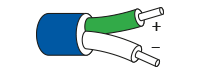
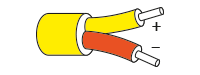
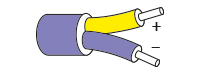
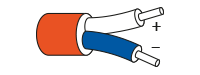
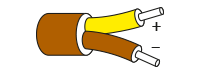
The most widely used colour code for Type K thermocouple cable is to the international IEC 60584-3 standard where the outer sheath is green, the positive NiCr conductor is also green and the negative NiAl conductor is colour coded white. Sometimes in the UK, American ANSI colours may be found which have a yellow outer sheath and yellow and red conductors as shown below. The colours of connectors for both match the outer sheath colour. You may also come across some old redundant colours such as the old BS1843 standard and these are shown in the table below:
| Thermocouple Type |
Extension and Compensating Cable Type | International Colour Code to IEC 60584-3 | American Colour Code to ANSI MC96.1 |
Redundant national colour coding for thermocouple cables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extension Cable |
Compensating Cable |
Thermocouple Cable Colour | Intrinsically Safe Colour | Connector Colour | |||||
| BS 1843 | DIN 43714 | NFC 42324 | |||||||
| K | KX |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| KCA |  |
||||||||
| KCB |  |
 |  | ||||||
More Information on Thermocouples
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a Type K thermocouple used for?
A Type K thermocouple is widely used for industrial, scientific, and general temperature measurement applications. It is commonly found in furnaces, kilns, engines, HVAC systems, metal processing, and food industry applications due to its high-temperature range and reliability. - Can you manufacture custom Type K thermocouples?
Yes — we manufacture custom Type K thermocouples in the UK, including bespoke lengths, diameters, sheaths, connectors, and terminations. Send your drawing or specification for a fast quotation or complete a Product Enquiry from any of our sensor pages. - Do you supply Type K thermocouple probes with calibration?
Yes — UKAS calibration and full traceability are available for all Type K probes. - What is the temperature range of a Type K thermocouple?
The typical temperature range of a Type K thermocouple is:
Continuous use: 0ºC to 1100ºC
Short-term exposure: -180ºC to 1350ºC
However, the practical range of any thermocouple also depends on factors like sheath material, wire thickness, and environmental conditions. - How accurate is a Type K thermocouple?
Accuracy as defined by the IEC 60584-1 standard is as follows:
Class 1: ±1.5ºC or 0.4% of the reading (whichever is greater)
Class 2: ±2.5ºC or 0.75% of the reading
Class 3: ±2.5ºC down to -167ºC
For maximum accuracy, calibration is recommended. - Why is Type K the most commonly used thermocouple?
Type K is the most popular thermocouple because it is: affordable compared to platinum-based thermocouples, durable in oxidizing atmospheres, capable of high-temperature measurements and widely available in different probe types. - Can Type K thermocouples be used in reducing atmospheres?
No, Type K thermocouples should not be used in reducing, sulfurous, or vacuum environments unless they are protected by a suitable sheath material. Type N thermocouples offer better stability in such conditions. - What is the output voltage of a Type K thermocouple?
The output voltage of a Type K thermocouple depends on temperature. Some approximate values (referenced to 0ºC) are:
100ºC → 4.096 mV
500ºC → 20.644 mV
1000ºC → 41.276 mV
For a detailed conversion, refer to the Type K Thermocouple Output Table. - What color code is used for Type K thermocouples?
IEC 60584-3 (International Standard) → Green outer sheath, green (+), white (-)
ANSI (USA Standard) → Yellow outer sheath, yellow (+), red (-) - What sheath materials are recommended for Type K thermocouples?
The choice of sheath material depends on the environment:
Stainless Steel 316 - General use, oxidation resistance
Inconel 600 - High-temperature applications up to 1250ºC
Ceramic Sheath - Extreme temperatures above 1300ºC
PFA/FEP Insulated - Low-temperature applications
For detailed information on sheath materials, please see our thermocouple sheath materials page. - How can I extend the life of a Type K thermocouple?
To maximize lifespan:
Use an appropriate sheath for the environment
Avoid exposure to reducing atmospheres
Use a proper cold junction compensation
Perform regular calibration - What is the difference between Type K and Type N thermocouples?
Both are nickel-based thermocouples, but Type N offers:
Better resistance to drift at high temperatures
Improved stability in reducing atmospheres
Less oxidation-related degradation
If high-temperature stability is required, Type N is preferred over Type K.

 France
France Germany
Germany Spain
Spain Netherlands
Netherlands Italy
Italy Hungary
Hungary United States
United States Australia
Australia